
Home page||Ship employment
||
Trim and stability booklet for cargo ships - how to use them
Commercial ships usually have a trim and stability booklet which may contain either curves of form or
hydrostatic tables and stability and trim characteristics for various conditions of loading. A typical trim and stability booklet will contain the following data:
i) Vessel characteristics,
including principal dimensions,
tonnage, location of
draft marks, builder, official
and registry numbers, etc.
ii) Instructions for use of the
nomograms, curves, and other
data in the booklet to calculate
stability and trim of the vessel
for given loading conditions.
iii) General operating instructions
and precautions.
iv) Tabulated tank and hold
capacities.
v) Hydrostatic properties (KM,
LCB, LCF, etc.) tabulated or
plotted as a function of mean
draft.
vi) Metacentric Height (GM) diagram, showing GM for tabulated conditions of loading and minimum required GM for vessel service.
vii) Trim diagram to calculate vessel trim when weights are added at locations other than the vessel center of gravity.
viii) Weight distribution and stability information for various conditions of loading.
ix) Liquid loading diagram, showing the location, capacity, and effect on list and trim of the ship’s tanks.
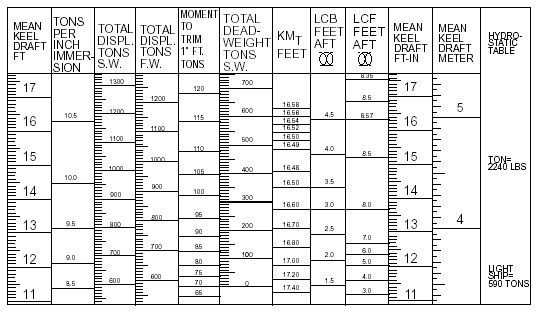
Figure shows a
typical hydrostatic table.
Related info:
Docking Plans , Reports & other structural plans for cargo ships
Other useful articles :
- Assigning loadlines marks
Loadlines are marks punched into and painted on the sides of general cargo ships.The assigning of the vessels loadline and the issue of the Certificate is the
responsibility of the Marine Authority of the country. .
More .....
-
Cargo ships Loaded Condition
closely monitor the ship's condition during cargo
operations to ensure that if a significant deviation from the agreed loading/unloading
plan is detected all cargo and ballast operations must STOP..
More .....
-
Packing a container recommended method
Packing a container should always be done on level plane either on the ground,on a railcar, or on a trailer. In the case of a trailer, care should be taken to ensure the trailer cannot tip whilst being packed especially if a forklift truck is being used. If necessary the trailer should be propped. Brakes should be securely applied and wheels choked.
More .....
- Packing principles relating to cargo in containers
Where relevant, stowing should be carried out in a sequence which will permit
rapid checking and storage operations during and after unloading. Should the
consignment include cargo subject to customs pre-entry procedures, customs
examination would be made easier and unloading avoided if the cargo were
stowed at the end of the container by the door.
More .....
- Container Securing guidance
Containers have very little strength in any direction other than vertically
through the corner posts thus it is necessary to provide substantial support
to the containers when they are on the ship. Stowage of containers is with
their longer dimension fore and aft since the ship motion transmitted to
cargo is greater in rolling than pitching and it is therefore prudent to limit
any possible cargo movement within the container to the shorter transverse
dimension.
More .....
- Trim and stability booklet for cargo ships
Contain either curves of form or hydrostatic tables and stability and trim characteristics for various conditions of loading
.
More .....
- Broken stowage? Cargo ships guideline
The access shall be separate from the hatchway opening, and shall be by a stairway if possible. A fixed ladder, or a line of fixed rungs, shall have no point where they fill a reverse slope
.
More .....
-
Ship type, design and facilities for cargo
Cargo gear is designed for speed and flexibility for handling breakbulk, palletized, or container cargo. Various combinations of derricks,
winches, and deck cranes are used for the handling of cargo. Cranes are fitted on many vessels to reduce manpower requirements. Some ships
have special heavy-lift derricks that may serve one or more holds. Booms are rigged for either yard and stay (burton) or swinging-boom
operation.
More .....
- Cargo ships structural plans- how to use them
Structural plans, sometimes called scantlings plans, show dimensions of the ships framing and plating. The midships section drawing, generally available for all ships
More .....
Machinery system main info pages
Home page||Cooling ||Machinery||Services ||Valves ||Pumps ||Auxiliary Power ||Propeller shaft ||Steering gears ||Ship stabilizers||Refrigeration||Air conditioning ||Deck machinery||Fire protection||Ship employment
||
Home ||
General Cargo Ship.com provide information on cargo ships various machinery systems -handling procedures, on board safety measures and some basic knowledge of cargo ships that might be useful for people working on board and those who working in the terminal. For any remarks please
Contact us
Copyright © 2010-2016 General Cargo Ship.com All rights reserved.
Terms and conditions of use
Read our privacy policy|| Home page||
