
Home page||Refrigeration system||
Comparison between refrigerants R717 ammonia & R744 carbon dioxide
R717 ammonia:
The ammonia used for refrigeration systems based on the use of a compressor,
condenser, expansion valve and an evaporator (Figure 11.2) is dry (anhydrous)
in that there is no water in solution with it. It has the chemical formula NH3 but
as a refrigerant, it is coded with the number R717.
The good qualities of
ammonia as a refrigerant have been offset by its toxicity, flammability and
pungent odour, so that carbon dioxide and then CFCs (which replaced CO2)
were used at sea in preference. Now that R12 is to be phased out in the short
term and R22 at a later date, ammonia is being considered as a replacement,
because despite its local harmful effects and disadvantages, it is ozone friendly.
The upper and lower explosive limits for pure ammonia in air, are 27% and
16% by volume, respectively. With oil contamination, the latter may reduce to
4%. Long-term exposure to ammonia should be restricted to the current
threshold limit value (TLV).
Exposure to higher concentrations of 1500 ppm
will result in damage to body tissue and death may result at 2500 ppm.
However, ammonia leaks are instantly detected at less than 10 ppm
concentration by the pungent odour and this is a safety feature. Very few
people can endure ammonia when its concentration exceeds the TLV. In the
liquid form, ammonia causes chemical and frost burns.
Corrosion of brass, bronze and similar alloys, occurs in ammonia systems if
there is any water present. These materials are avoided with steels being used
instead.
Ammonia is highly soluble in water with which it forms ammonium
hydroxide, a weak base. About 1300 volumes of ammonia can be dissolved in I
volume of water at low temperature. However it is easily expelled by boiling.
This action makes the vapour absorption refrigerator possible. Refrigerators, of
this type do not require a compressor for operation, only a heat source.
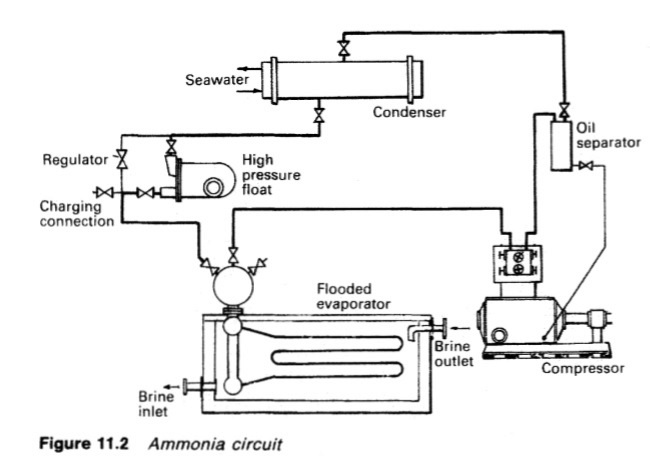
Figure : Ammonia circuit
R744 carbon dioxide
When carbon dioxide (CO2) is used as a refrigerant the working pressures are
high, being about 70 bar at the compressor discharge and 20 bar at the
compressor suction. The machinery and system must therefore be of
substantial construction. The critical temperature is low (31 degC) and this causes
problems in areas with high sea-water temperature. It also has a low coefficient
of performance. Poor miscibility with oil required that a drain system be
provided to remove oil continuously from the evaporator.
The gas is not explosive or flammable but a leak is potentially dangerous
because it can displace air and asphyxiate. It is also toxic. The liquid is stored in
steel bottles at high pressure, ideally in a cool space. A temperature rise will
cause a pressure rise in the bottles which is relieved by the rupturing of a safety
disc and release of gas.
Summarized below various refrigeration system components, working process and maintenance guideline:
- Automatic direct expansion refrigeration- vapour compression
The basic components of any refrigeration system (Figure 11.1) working on the
vapour compression cycle, are the compressor, condenser, expansion valve,
evaporator and the refrigerant fluid which is alternately vaporized and liquefied
during the refrigeration cycle. The temperature at which a fluid boils or
condenses, is known as the saturation temperature and varies with pressure....more
-
Choice of refrigerants
Theoretically, almost any liquid can be used as a refrigerant if its pressure/temperature relationship is suitable for the conditions. Although no perfect refrigerant is known, there are certain factors which determine a refrigerant's desirability for a particular duty and the one selected should possess as many as possible of the following
characteristics.....more
-
Refrigeration systems - Chamber cooling arrangements
To avoid having an extended refrigeration circuit for cargo cooling, a brine system can be used. The brine is cooled by the evaporator and in turn cools grids or batteries. Grids provide cooling which relies on convection and conduction but air circulated through brine batteries provides a positive through cooling effect.
.....more
-
Refrigeration system components
Marine condensers are generally of the shell and tube type, designed for high pressures. There may a few coil-in-casing or other types still in use. The coolant passes through the tubes with refrigerant condensing on the outside......more
-
Refrigeration system compressors
Refrigeration compressors are usually either reciprocating, or of the rotary
screw displacement type. Centrifugal and rotary vane compressors have also
been used.....more
-
Refrigeration systems expansion valves
The expansion valve is the regulator through which the refrigerant passes from the high pressure side of the system to the low pressure side. The pressure drop causes the evaporating temperature of the refrigerant to fall below that of the evaporator. .....more
- Monitoring instruments,CO2 measurement & Heat leakage and insulation test
All necessary cargo temperature readings are obtained on modern reefers and container ships on a data logger which makes an automatic record. The temperatures and pressures relating to refrigerant gas and liquid, cooling water, brine and the ambient are also required. Most of these are obtained from direct reading instruments.
.....more
- Marine condenser assembly
The temperature of the refrigerated spaces with a direct expansion system is controlled between limits through a thermostatic switch and a solenoid valve which is either fully open to permit flow of refrigerant to the room evaporator, or closed to shut off flow. The solenoid valve is opened when the sleeve moving upwards due to the magnetic coil hits the valve spindle tee piece and taps the valve open.....more
- Comparison between refrigerants R717 ammonia & R744 carbon dioxide
The ammonia used for refrigeration systems based on the use of a compressor,
condenser, expansion valve and an evaporator (Figure 11.2) is dry (anhydrous)
in that there is no water in solution with it. It has the chemical formula NH3 but
as a refrigerant, it is coded with the number R717....more
-
Container cooling system
The air is cooled either by brine or direct expansion batteries and the containers are arranged so that one cooler can maintain a stack of containers at a given temperature. The temperature of the return air duct for each container is monitored.....more
Home page||Cooling ||Machinery||Services ||Valves ||Pumps ||Auxiliary Power ||Propeller shaft ||Steering gears ||Ship stabilizers||Refrigeration||Air conditioning ||Deck machinery||Fire protection||Ship design
||Home ||
General Cargo Ship.com provide information on cargo ships various machinery systems -handling procedures, on board safety measures and some basic knowledge of cargo ships that might be useful for people working on board and those who working in the terminal. For any remarks please
Contact us
Copyright © 2010-2016 General Cargo Ship.com All rights reserved.
Terms and conditions of use
Read our privacy policy|| Home page||
