
Home page||Steering gears ||
Rudder carrier bearing & Steering gear arrangement for cargo ship
The rudder carrier bearing (Figure below) takes the weight of the rudder on a
grease lubricated thrust face. The rudder stock is located by the journal
beneath, also grease lubricated.
Support for the bearing is provided by framing beneath the steering gear
deck. There is thicker deck plating in the area beneath the carrier bearing and
the latter may be supported on steel chocks. The base of the carrier bearing is
located by side chocks welded to the deck. The carrier may be of meehanite
with a gunmetal thrust ring and bush. Carrier bearing components are split as
necessary for removal or replacement. Screw down (hand) lubricators may be
fitted but automatic lubricators are common. The grease used for lubrication is
of a water resistant type (calcium soap base with graphite).
The tiller (Figure 9.1) is keyed to the rudder stock and is of forged or cast
steel with one (or two for a four ram gear) arms, machined smooth to slide in a
swivel block arrangement designed to convert linear movement of the rams to
the rotary movement of the tiller arms and rudder stock. This particular device,
known as a Rapson slide, is used for many, but not all, ram type gears. The rams
are one-piece steel forgings, with the working surface ground to a high finish.
Each pair of Rapson slide rams, is bolted together, the joined ends being bored
vertically and bushed to form top and bottom bearings for the projecting
spigots on the swivel block. Crosshead slippers, bolted to the face of the central
section of the rams, slide on the machined surfaces of the guide beam. Guide
beams also serve to brace each pair of cylinders against the tendency for them
to be pushed apart by the hydraulic pressure. The cylinders have substantial
feet bolted to the stools on which the gear is mounted.
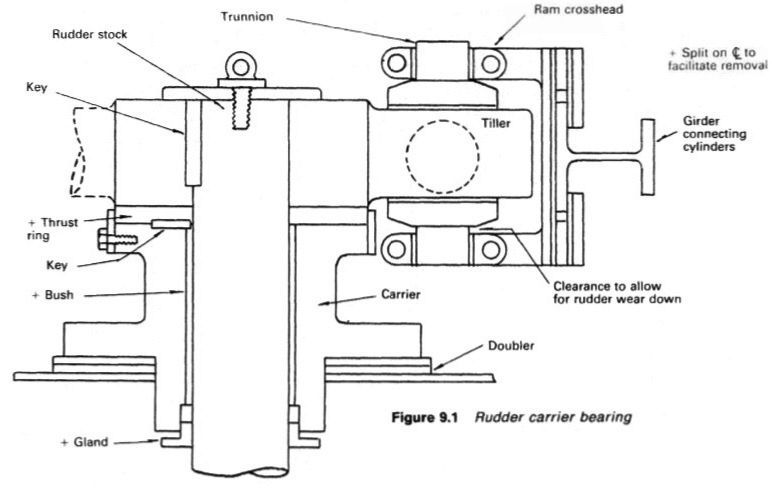
Figure : Rudder carrier bearing
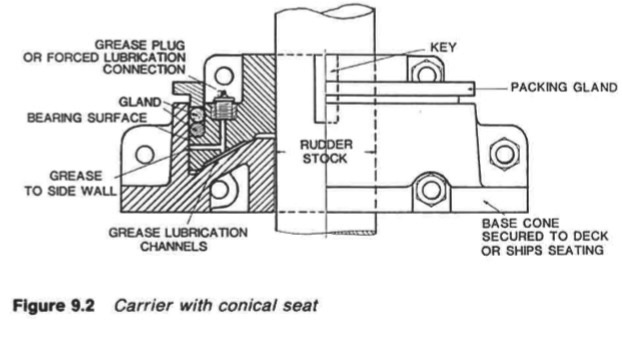
Figure : Carrier with conical seat
Weardown of the carrier bearing is monitored by periodically measuring the
clearance marked. The original clearance is usually about 20mm.
An alternative type of carrier bearing with a conical seat (Figure 9.2) has the
advantage that the seat and side wall will locate the rudder stock. The angle of
the conical seat is shallow to prevent binding.
Bearing weardown occurs over a period of time, and allowance is made in
the construction of the steering gear (see Figure 9.1) for a small vertical drop of
the rudder stock. This weardown allowance is checked periodically and
restored as necessary. Lifting of the rudder and stock by heavy weather can be
limited by jumping stops between the upper surface of the rudder and the stern
frame.
The usual limit for movement of the rudder, is 35° each way from the mid
position and this is controlled by the telemotor. External rudder stops if fitted,
would limit movement to, say, 39° from the mid position. The steering gear
itself will also impose a limit on rudder movement but with hydraulic oil loss
and the ship stopped in heavy weather, there may be severe damage to the
gear. The telemotor control imposes the usual 35° limit.
Summarized below various ship steering gears general guideline:
- Ship Steering gear failures and safeguards
The hydraulic circuit incorporates an arrangement of stop and bypass valves in the chest VC, which enable the gear to be operated on all four or on any two adjacent cylinders but not with two diagonally disposed cylinders.
......
- Four-ram electro-hydraulic steering gear mechanism
The hydraulic circuit incorporates an arrangement of stop and bypass valves in the chest VC, which enable the gear to be operated on all four or on any two adjacent cylinders but not with two diagonally disposed cylinders.
......
- Enclosed hunting gear
The light construction of the combined control and hunting gears is possible
because the forces concerned are moderate. The self-contained unit is
self-lubricating, and contained in an oil-tight case.
......
- Ship steering control mechanism- use of Hydraulic telemotor
The telemotor has become, on many vessels, the stand-by steering control
mechanism, used only when the electric or automatic steering fails. It comprises
a transmitter on the bridge and a receiver connected to the steering gear
variable delivery pump, through the hunting gear.
......
- Two-ram electro-hydraulic steering gear with variable
delivery pumps
An arrangement of a two-ram steering gear with variable
delivery pumps may have a torque capacity of 120-650 kNm.
The cylinders for this gear are of cast steel but the rarns comprise a one-piece
steel forging with integral pins to transmit the movement through cod pieces
which slide in the jaws of a forked tiller end.
......
- Rudder carrier bearing & Steering gear
The rudder carrier bearing takes the weight of the rudder on a
grease lubricated thrust face. The rudder stock is located by the journal
beneath, also grease lubricated
......
- Small hand and power gears - Ship steering systems
A simpler variant of the electro-hydraulic gear, for small ships requiring rudder
torques below say, 150 kNm
......
- Four ram gear with servo-controlled axial cylinder pumps
Variants of the servo-controlled swash plate axial cylinder pump
are capable of working at 210 bar. Each pump is complete with its own torque
motor, servo-valve, cut-off mechanism, shut-off valve and oil cooler.
......
- Vane type gear - provides security of four ram steering gear
These may be regarded as equivalent to a two-ram gear, with torque capacities
depending on size. An assembly of two rotary vane gears, one above the other,
provides the security of a four ram gear.
......
- Details of two ram hydraulic steering gear arrangement
When the main pumps are at no-stroke, the auxiliary pumps dischar.
to the reservoir via a pressure-limiting valve PC20, set at 20 bar, and to t
pump casings. When the main pumps are on-stroke, the auxiliary pump
discharge to the main pump suction.
......
Home page||Cooling ||Machinery||Services ||Valves ||Pumps ||Auxiliary Power ||Propeller shaft ||Steering gears ||Ship stabilizers||Refrigeration||Air conditioning ||Deck machinery||Fire protection||Ship design
||Home ||
General Cargo Ship.com provide information on cargo ships various machinery systems -handling procedures, on board safety measures and some basic knowledge of cargo ships that might be useful for people working on board and those who working in the terminal. For any remarks please
Contact us
Copyright © 2010-2016 General Cargo Ship.com All rights reserved.
Terms and conditions of use
Read our privacy policy|| Home page||

