
Home page||Valves & pipelines ||
Cocks and valves - Ship service systems
Cocks and valves are designed to control or interrupt flow. This is done in cocks by rotating the plug, and in valves by lowering, raising or rotating a disc in relation to a seating surface or by controlling the movement of a ball. These fittings have bodies furnished with flanged or screwed ends (or ends prepared by welding) for connection to the joining pipes.
Cocks:>
A cock may be straight-through, right-angled or open-bottomed as required by its situation in a pipe system. Its plug may be tapered or parallel with tightness achieved by lapping in or by resilient packing material (Figure below) often in the form of a ready made sleeve.
In machinery spaces, the short sounding pipes for fuel or lubricating oil tanks, must be fitted with cocks having parallel as opposed to tapered plugs. This, together with the requirement for weighted handles which will automatically close the cock when released, is for safety. Tapered plugs, when tightened to hold the cock open for sounding and then forgotten, have contributed to fires when tanks have overflowed. Boiler blowdown cocks on the ship's shell, are constructed so that the handle can be removed only when the cock is closed.
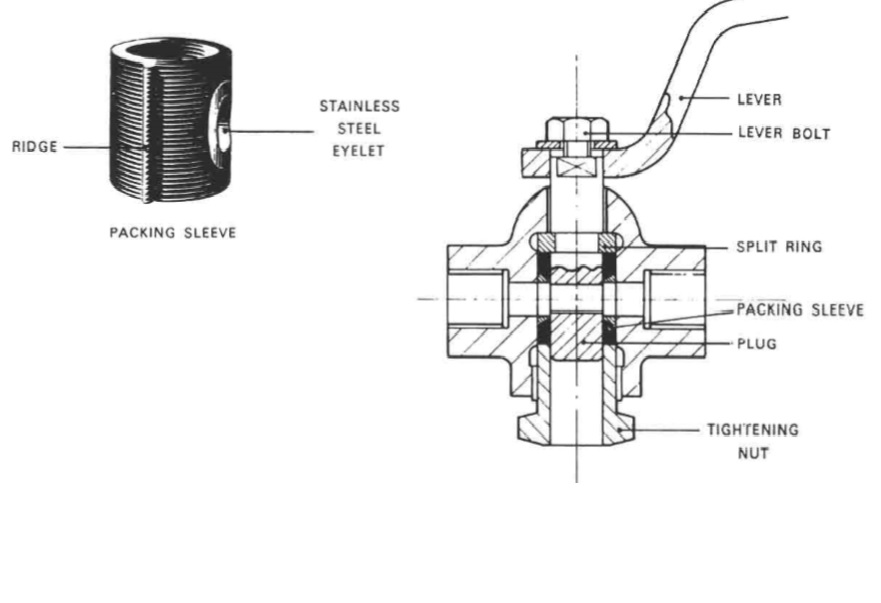
Figure : Example of a sleeve-packed cock (Richard Klinger Ltd)
Summarized below some of the basic procedure of machinery valves & pipeline systems :
- Valves & pipeline materials corrosion & erosion
Galvanic corrosion is a major challenge for any pipes which carry sea water. Rust is a particular corrosion problem for steel pipes exposed to contact with sea water or moisture generally and air. Pipe runs along tank tops or on deck, are examples of the latter. Steel pipes in these areas require external as well as internal protection.....
- valves-&-pipelines-strength-of-materials
The strength of materials used for pipes and fittings must be adequate for the
system pressures and possible over-pressures. Pipelines and valves, for
example, used to carry and control the flow of high temperature, high pressure
steam must obviously be made to very exacting specifications by approved
manufacturers.....
- Valves & pipelines-system cleaning & draining
It is often found, in new ships, that the bilges and bilge systems have not been
thoroughly cleaned with the result that wood, nuts, bolts, rags and other debris
are found inside valves and pipes after initial bilge pumping. These choke the
valve-chests and prevent the valves from being properly closed. They also
block strainers. ....
- Expansion arrangements
Provision must be made in pipe systems to accommodate changes in length due to change of temperature, and so prevent undue stress or distortion as pipes expand or contract.....
- Valves & cocks
Cocks and valves are designed to control or interrupt flow. This is done in cocks by rotating the plug, and in valves by lowering, raising or rotating a disc in relation to a seating surface or by controlling the movement of a ball. ...
- Butterfly valves
A butterfly valve consists basically of a disc pivoted across the bore of a ring body having the same radial dimensions as the pipe in which it is fitted.....
- Gate valves
Unlike the globe valve, gate (or sluice) valves give full bore flow without change of direction. The valve disc known appropriately as a gate,....
- Globe valves
The globe valve has a bulbous body, housing a valve seat and screw down plug or disc arranged at right angles to the axis of the pipe....
- Relief valves
Excess pressure is eased by a relief valve . This consists of a disc held closed by a spring loaded stem. The compression on the spring can be adjusted so that the valve opens at the desired pressure. ....
- Valves traps
A steam trap is a special type of valve which prevents the passage of steam but allows condensate through. It works automatically and is used in steam heating lines to drain condensate without passing any steam. ....
- Flap valves & valve chest
Scupper pipes from accommodation spaces are fitted with non-return valves. Those scuppers from spaces below the bulkhead deck, are required to be fitted with non-return valves which can be positively closed from above the bulkhead deck or, if this is not practical, with two non-return valves.....
- Quick closingvalves
Fuel oil service and some other tanks must be fitted with valves that can be closed rapidly and remotely in the event of an emergency such as fire. Wire operated valves are commonly fitted,....
- Strainers & filters
The term strainer is sometimes used specifically for a simple device made up with a single layer of coarse gauze, a very coarse wire mesh or a drilled or perforated plate. ...
Home page||Cooling ||Machinery||Services ||Valves ||Pumps ||Auxiliary Power ||Propeller shaft ||Steering gears ||Ship stabilizers||Refrigeration||Air conditioning ||Deck machinery||Fire protection||Ship design
||Home ||
General Cargo Ship.com provide information on cargo ships various machinery systems -handling procedures, on board safety measures and some basic knowledge of cargo ships that might be useful for people working on board and those who working in the terminal. For any remarks please
Contact us
Copyright © 2010-2016 General Cargo Ship.com All rights reserved.
Terms and conditions of use
Read our privacy policy|| Home page||
