
Home page||Marine Pumps ||
Marine pumps
Erosion by abrasives
A pump handling liquids which contain abrasives, will suffer erosion on all internal surfaces, including bearings and shaft seals. The sea-water circulating pumps of ships operating in waters that contain large quantities of silt and sand
require frequent renewal of shaft seals or packing, also of shaft sleeves in way of the gland and bearings.
Impellers are sometimes extensively damaged with resulting perforations and massive enlargement of wear ring clearance. Pump casings suffer erosion on all internal surfaces. Impellers and wear rings may have to be changed frequently and casings may need to be renewed at longer intervals.
Special provision can be made in such pumps or those employed in suction dredgers (Figure 1) to safeguard bearings and shaft seals. The protection is provided by a water service to the shaft which washes solids away from the shaft seal area. Bearings can be protected by being mounted external to the casing.
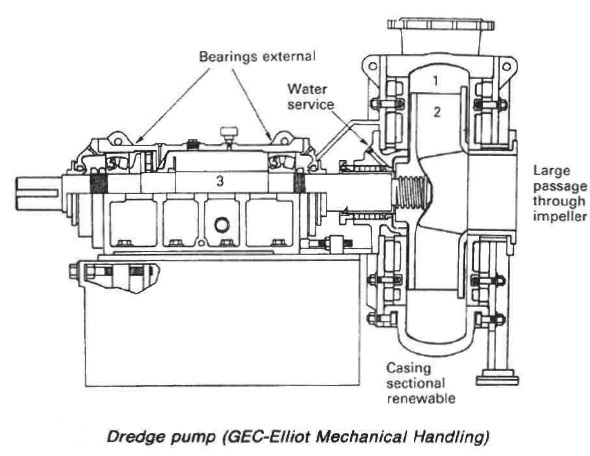
Figure 1: Dredge pump
The pumps designed for use in suction dredgers require frequent casing repairs: a solution has been provided by one manufacturer with a casing which is built from renewable parts. Erosion due to cavitation as opposed to the presence of abrasives is selective. The problem occurs, as with cavitation damage on propeller blades, in certain areas where cavitation pockets or bubbles collapse.
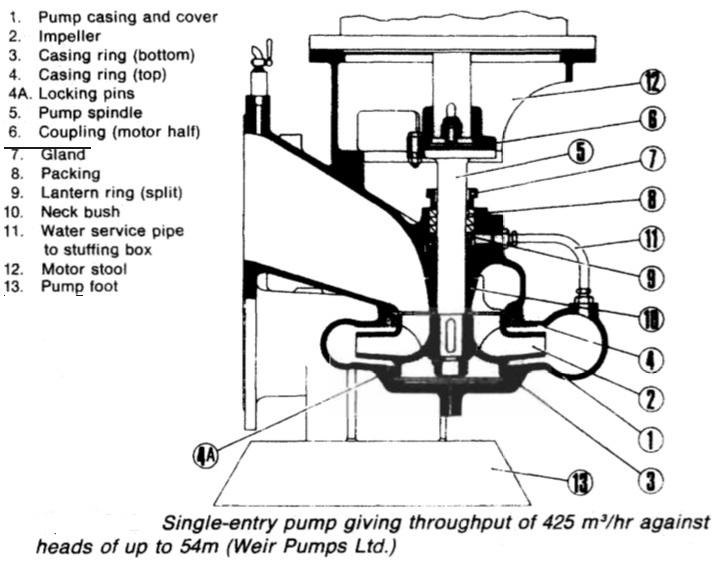
Figure 2: Single entry pump
Figure 2 : Single-entry pump giving throughput of 425 m3/hr against heads of up to 54m (Weir Pumps Ltd.)
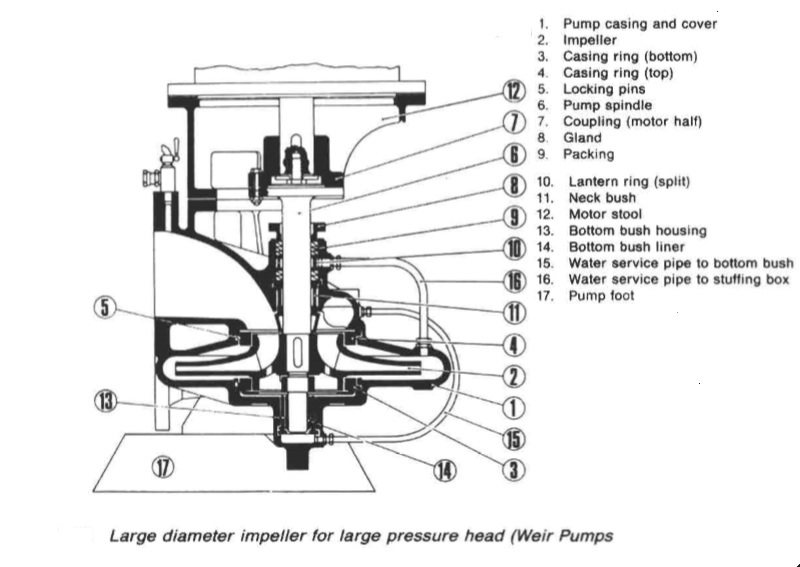
Figure 3: Large diameter impeller for large pressure head
Figure 3; Large diameter impeller for large pressure head (Weir Pumps Ltd.)
Summarized below some of the basic procedure of marine pumps and pumping system onboard :
- Axial flow pumps
An axial flow pump is one in which a screw propeller is used to create an increase in pressure by causing an axial acceleration of liquid within its blades. The incidental rotation imparted to the liquid is converted into straight axial movement by suitably shaped outlet guide vanes.....
- centrifugal pumps
Rotation of a centrifugal pump impeller causes the liquid it contains to move outwards from the centre to beyond the circumference of the impeller. The revolving liquid is impelled by centrifugal effect.....
- Centrifugal pump cavitation
Because of their self-priming ability, positive displacement pumps are widely used for lubricating oil duties. This practice is completely satisfactory in installations where the pump speed is variable but when the pump is driven by a constant speed a.c. motor it is necessary to arrange a bypass which can be closed in to boost flow. ....
- Gear pumps
Diesel engine and gearbox lubrication systems are normally supplied by gear
pumps which are independently driven for large slow speed engines and
stand-by duties but usually shaft driven for medium and high speed engines.
Gear pumps are also used for fuel and oil transfer, boiler combustion systems
and other duties.....
- General pumping system characteristics
A pump divides its pipe system into two distinct parts, each with different
characteristics. These are the suction and discharge sides. On the suction side
the drop in pressure that can be produced by a pump is limited to that of an
almost perfect vacuum. On the discharge side there is theoretically, no limit to
the height through which a liquid can be raised.....
- General purpose pumps
Single entry general purpose pumps are used for salt and fresh water circulating and also for bilge and ballast duties. The impeller is suspended from the shaft with no bottom support. ....
- Lobe pumps
Lobe pumps as manufactured by Stothert and Pitt have inner and outer
elements which rotate in a renewable liner fitted in the pump body. The inner
rotor is eccentric to the outer and is fitted to a shaft located by bearings in the
pump covers....
- Marine pumps construction
Marine pumps are usually installed with the shaft vertical and the motor above the pump. This positions the pump as low as possible for the best NPSH, takes up the least horizontal space and leaves the electric motor safer from gland or other leakage.....
- Pumps erosion
A pump handling liquids which contain abrasives, will suffer erosion on all internal surfaces, including bearings and shaft seals. The sea-water circulating pumps of ships operating in waters that contain large quantities of silt and sand
require frequent renewal of shaft seals or packing, also of shaft sleeves in way of the gland and bearings.....
- Rotary displacement pump
Positive displacement rotary pumps rely on fine clearances between moving
parts for their efficient operation. Excessive wear or erosion of parts, due to
friction contact or the presence of abrasives, is avoided by employing this type
of pump for specialized rather than general duties......
- Screw pumps
Both double-screw pumps, in which the screws are driven in phase by timing
gears , and triple screw pumps , in which the centre
screw is driven and the outer screws idle are used at sea especially for pumping
high viscosity liquids such as oil and some liquid cargoes.....
Home page||Cooling ||Machinery||Services ||Valves ||Pumps ||Auxiliary Power ||Propeller shaft ||Steering gears ||Ship stabilizers||Refrigeration||Air conditioning ||Deck machinery||Fire protection||Ship design
||Home ||
General Cargo Ship.com provide information on cargo ships various machinery systems -handling procedures, on board safety measures and some basic knowledge of cargo ships that might be useful for people working on board and those who working in the terminal. For any remarks please
Contact us
Copyright © 2010-2016 General Cargo Ship.com All rights reserved.
Terms and conditions of use
Read our privacy policy|| Home page||


